A
File System is an organizational method that the operating system uses to store information on a disk drive. In other words, your operating system needs to organize a hard drive so that it can easily store and retrieve things.
Windows XP supports two primary file systems:
NTFS and
FAT. Let's understand in brief what these two file systems mean and then we will find out which file system we use on our PC.
FAT file system:
FAT which stands for "File Allocation Table" has two variants:
FAT 16 and
FAT 32. The difference between the two is how they allocate space and the size of the hard drive partitions they can access. FAT 16 can access drive partitions up to 2GB and can store only up to 512 entries in the root directory. FAT 32 can access drive partitions up to 32GB in size and has no limit on the number of files that can be stored in the root directory.
NTFS file system:
NTFS which stand for "New Technology File System" is the default file system for hard drives in a Windows XP. It is used in instances when you need increased file security or you share your data with others over a network. NTFS can access drive partitions up to 2TB (terabytes) in size which is 62.5 times larger than the largest partition accessible by FAT 32.
Now that we have an idea about FAT and NTFS, lets learn to identify the type of system that we use.
Click the "Start" button on the taskbar. Followed which, right click on "My Computer" and select "Manage".
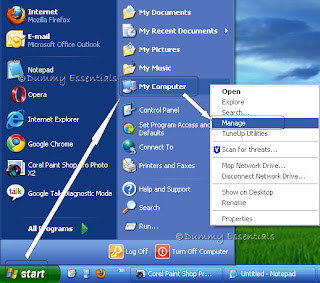
In the "Computer Management" window that opens, click on the (+) before "Storage"
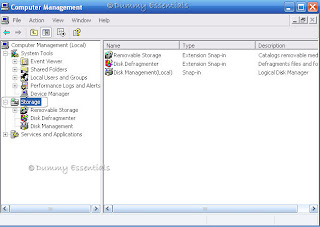
Finally, click on the "Disk Management" option.
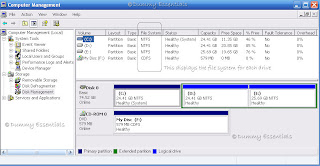
A list of your disk drives appears at the right side of the Computer Management window. At the top right you see a list of all your system’s drives. The File System column indicates the file system used for the drive. (Different drives can use different file systems.)

 In the "Computer Management" window that opens, click on the (+) before "Storage"
In the "Computer Management" window that opens, click on the (+) before "Storage"
 Finally, click on the "Disk Management" option.
Finally, click on the "Disk Management" option.
 A list of your disk drives appears at the right side of the Computer Management window. At the top right you see a list of all your system’s drives. The File System column indicates the file system used for the drive. (Different drives can use different file systems.)
A list of your disk drives appears at the right side of the Computer Management window. At the top right you see a list of all your system’s drives. The File System column indicates the file system used for the drive. (Different drives can use different file systems.)